10 Dec Difference between Isolators and Biological Safety Cabinets.
Biological Safety Cabinets (BSCs) and Isolators are two examples of containment cabinets frequently used in the pharmaceutical sector. These two tools were developed to protect lab personnel from breathing in hazardous substances and to stop contagious microorganisms from spreading across the workspace.
Isolator:
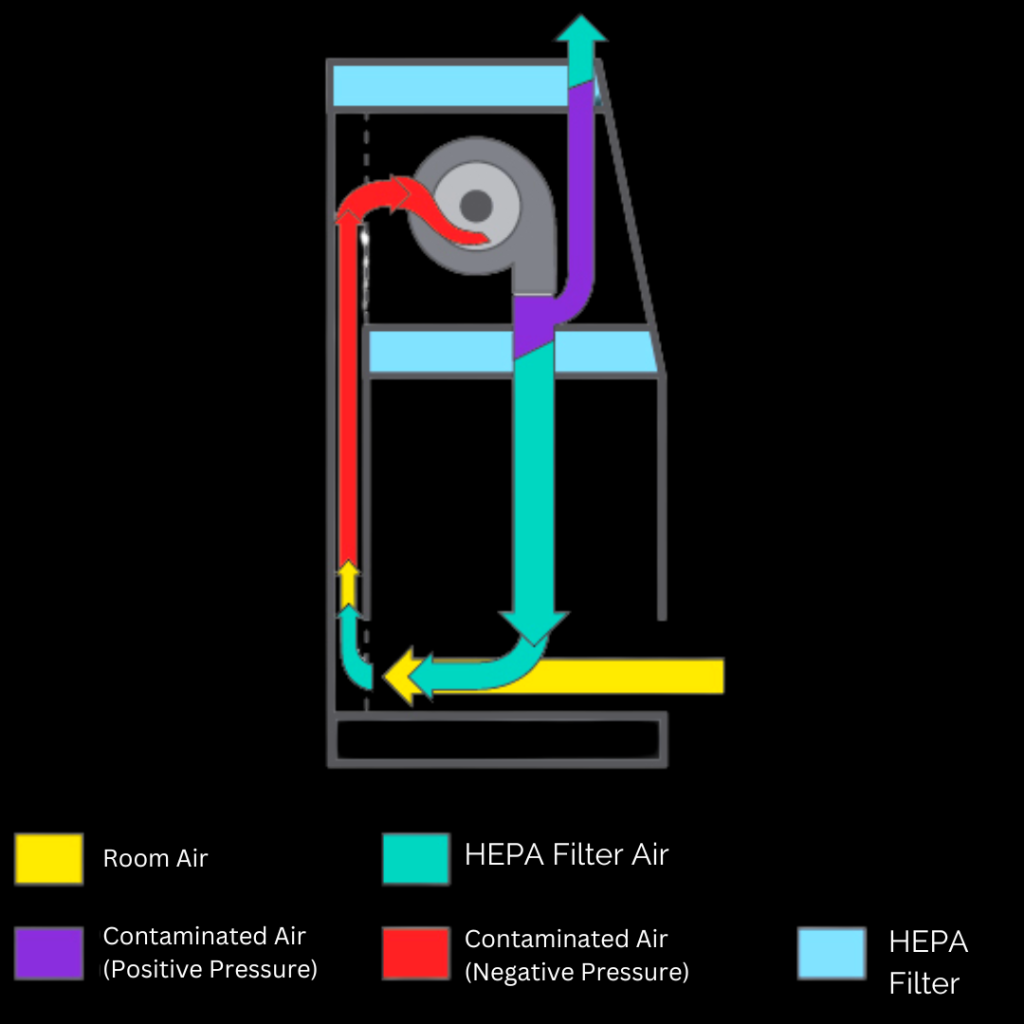
The aseptic containment isolator is also known as the laminar flow glovebox isolator. By creating a whole barrier between the material and the technician, these containment isolators give pharmacy personnel a way to handle materials throughout the compounding and material transfer processes. In order to prevent polluted air from being pumped back into the lab, a series of HEPA filters are used.
This barrier isolator offers a clean and secure environment for handling both hazardous and non-hazardous materials. A Compounding Aseptic Isolator (CAI) is used to produce a positive pressure controlled environment while dealing with non-hazardous materials. A Compounded Aseptic Containment Isolator (CACI) is used to establish a negative pressure controlled environment for handling hazardous materials.
Biological Safety Cabinets (BSCs):
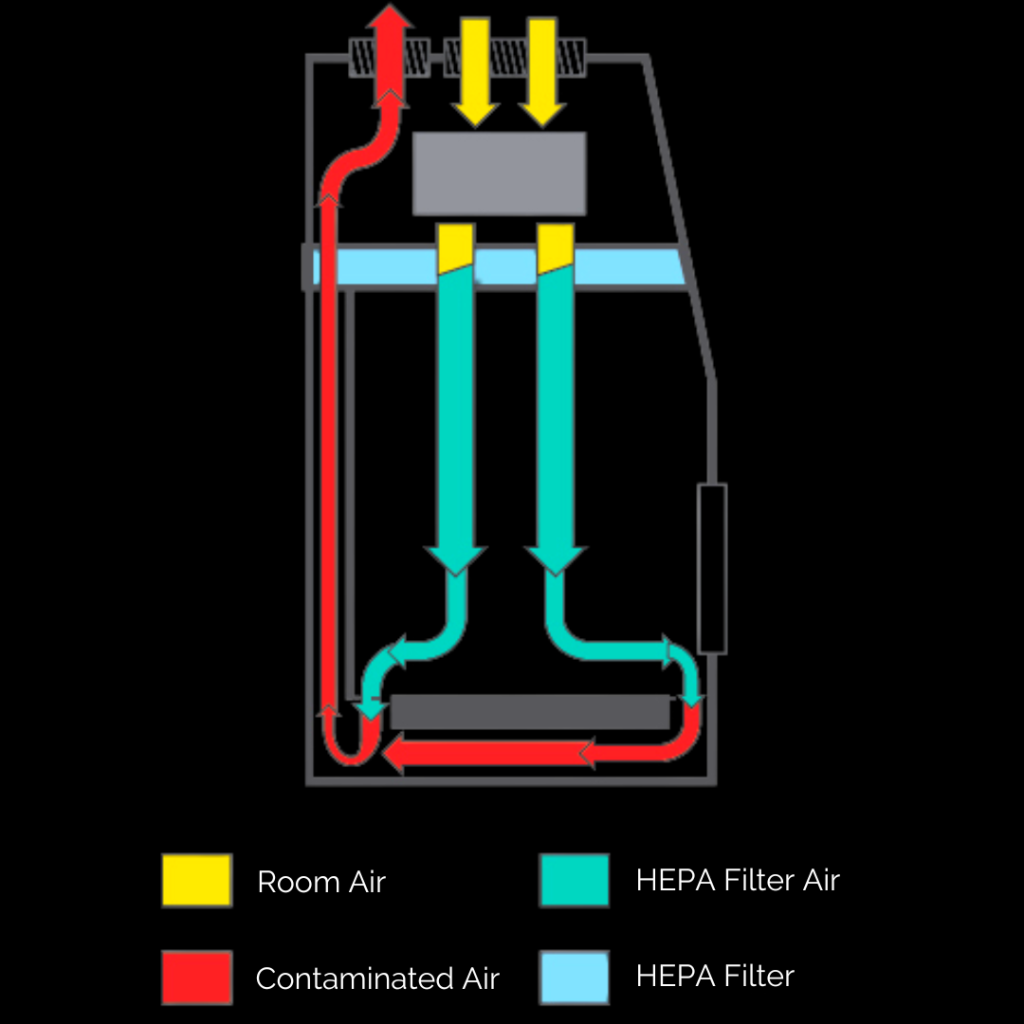
When handling disease microorganisms, human or animal tissue, recombinant DNA, transgenic plants, human gene studies, or genetically modified microorganisms, biological safety cabinets, or BSCs, are frequently employed in research facilities. Laminar air flow is used in biosafety cabinets to protect lab technicians and the surrounding area from biohazard exposure.
There are three different classes of BSCs: Class I, Class II, and Class III. The lowest degree of safety is provided by Class I for handling low to moderate risk biohazards, Class II for handling low, moderate, and high-risk microorganisms, and Class III for handling high-risk infectious agents. HEPA filters are used in Class II and Class III to eliminate minute impurities from the air being cycled back into the laboratory.
Pros and Cons of Isolator and Biological Safety Cabinets:

Concluding the blog:
Both Isolators and Biological Safety cabinets are safe options to use in research laboratories limiting exposure of lab personnel, providing a clean work environment, The major difference between them is Biological safety cabinets (Class I and II) have a front opening that increases the risk of pathogens escaping the cabinet through it. These biological cabinets are not ideal when handling moderate to high-risk hazardous material.
To know more about Isolators and Biological Safety Cabinets, connect with us at sales@isovax.in



Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.